Hydrogeology of Cameroon
Africa Groundwater Atlas >> Hydrogeology by country >> Hydrogeology of Cameroon
Most of the textual information on this page was taken from the chapter on Cameroon in the report [‘Groundwater in North and West Africa’ (UN 1988). This information is outdated. If you have more recent information on the hydrogeology of Cameroon, please get in touch.
Compilers
Dr Kirsty Upton and Brighid Ó Dochartaigh, British Geological Survey, UK
Geographical Setting

General
Cameroon is in central-west Africa with a western coast on the Gulf of Guinea, and Lake Chad at its northernmost extent. Its geography includes a coastal plain, which extends 15 to 150 km inland; the south Cameroon plateau which rises from the coastal plain to more than 600 m; the Cameroon chain of mountains, hills and plateaus that extends from Mount Cameroon on the coast(Cameroon's highest point at 4,095 m) almost to Lake Chad on the northern border; the Adamawa Plateau in the centre of the country, with an average elevation of 1,100 m; and a northern lowland region which extends from the edge of the Adamawa Plateau to Lake Chad, with an elevation of around 300 m.
| Estimated Population in 2013* | 22,253,959 |
| Rural Population (% of total) (2013)* | 46.8% |
| Total Surface Area* | 472,710 sq km |
| Agricultural Land (% of total area) (2012)* | 20.6% |
| Capital City | Yaoundé |
| Region | Central Africa |
| Border Countries | Nigeria, Chad, the Central African Republic, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, the Republic of the Congo. |
| Annual Freshwater Withdrawal (2013)* | 966.4 Million cubic metres |
| Annual Freshwater Withdrawal for Agriculture (2013)* | 76.3% |
| Annual Freshwater Withdrawal for Domestic Use (2013)* | 16.7% |
| Annual Freshwater Withdrawal for Industry (2013)* | 7.1% |
| Rural Population with Access to Improved Water Source (2012)* | 51.9% |
| Urban Population with Access to Improved Water Source (2012)* | 94.1% |
* Source: World Bank
Climate
The climate varies across the country, controlled by topography. The upland areas have a mild climate with high rainfall. The coast is hot and very wet, with only a short dry season. The plateau areas show distinct wet and dry seasons, with lower rainfall than the coastal region. The northern lowland region is relatively arid, with low rainfall and high temperatures.
-
Koppen Geiger Climate Zones
-
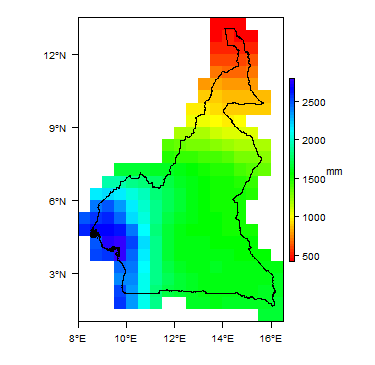
Average Annual Precipitation
-
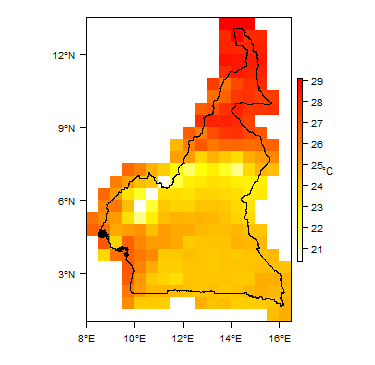
Average Temperature
For further detail on the climate datasets used see the climate resources section.
Surface water
| The main rivers in the south of the country are the Ntem, Nyong, Sanaga, and Wouri, which flow southwestward or westward into the Gulf of Guinea. The Dja and Kadéï drain southeastward into the Congo River. In the north, the Bénoué River flows north and west into the Niger. The Logone flows northward into Lake Chad, which Cameroon shares with three neighbouring countries. |  |
Soil
 |
Land cover
| The coastal plain and southern plateau is dominated by equatorial rainforest. The upland regions have highland forest type vegetation. The dominant land cover in the northern lowland region is savanna scrub and grass.
|
 |
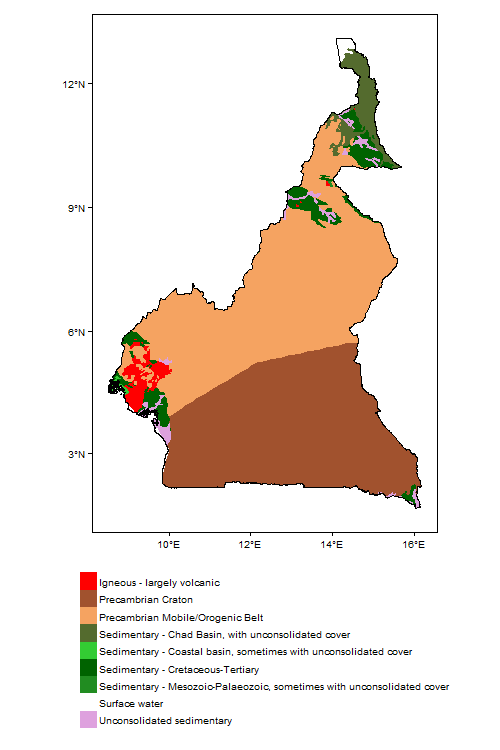
Geology
This section provides a summary of the geology of Cameroon. More information is available in the report Groundwater in North and West Africa: Cameroon (1988) (see References section, below).
The geology map shows a simplified version of the geology at a national scale (see the Geology resources page for more details).
| Key Formations | Period | Lithology | Structure |
| Geological Environment 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name of formation1 | Time period | Description | Structure |
| Geological Environment 2 | |||
| Geological Environment 3 | |||
Hydrogeology
This section provides a summary of the hydrogeology of the main aquifers in Cameroon. More information is available in the report Groundwater in North and West Africa: Cameroon (1988) (see References section, below).
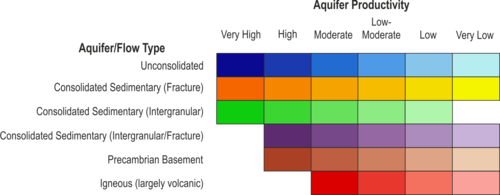
The hydrogeology map shows a simplified version of the type and productivity of the main aquifers at a national scale (see the Aquifer properties resource page for more details).
Unconsolidated
| Named Aquifers | Period | General Description | Water quality |
Sedimentary - Intergranular Flow
| Named Aquifers | Period | General Description | Water quality |
Sedimentary - Intergranular & Fracture Flow
| Named Aquifers | Period | General Description | Water quality |
Sedimentary - Fracture Flow
| Named Aquifers | Period | General Description | Water quality |
Basement
| Named Aquifers | Period | General Description | Water quality |
Groundwater Status
Groundwater quantity
Groundwater quality
Groundwater use and management
Groundwater use
Groundwater management
Groundwater monitoring
Transboundary aquifers
For further information about transboundary aquifers, please see the Transboundary aquifers resources page
References
The following references provide more information on the geology and hydrogeology of Cameroon.
These, and others, can be accessed through the Africa Groundwater Literature Archive
United Nations. 1988. Groundwater in North and West Africa: Cameroon. United Nations Department of Technical Cooperation for Development and Economic Commission for Africa, Natural Resources/Water Series No. 18, ST/TCD/5.
Return to the index pages
Africa Groundwater Atlas >> Hydrogeology by country >> Hydrogeology of Cameroon